Server Operations
After registering the Windchill server with Creo Parametric, you can start accessing the data on the Windchill servers. The Creo Parametric interaction with Windchill servers leverages the following locations:
| • | Commonspace (Shared folders) |
| • | Workspace (Server-side workspace) |
| • | Workspace local cache (Client-side workspace) |
| • | Creo Parametric session |
| • | Local disk |
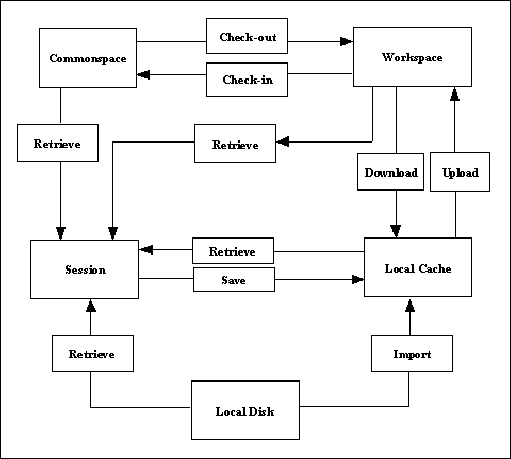
The methods described in this section enable you to perform the basic server operations. The following illustration shows
how data is transferred among these locations.
Upload
An upload transfers Creo Parametric files and any other dependencies from the local workspace cache to the server-side workspace.
Methods Introduced:
The method pfcServer.UploadObjects() uploads the object to the workspace. The object to be uploaded must be present in the current Creo Parametric session. You must save the object to the workspace using pfcModel.Save()pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS before attempting to upload it.
The method pfcServer.UploadObjectsWithOptions() uploads objects to the workspace using the options specified in the pfcUploadOptions class. These options allow you to upload the entire workspace, auto-resolve missing references, and indicate the target folder
location for the new content during the upload. You must save the object to the workspace using pfcModel.Save(), or import it to the workspace using pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() before attempting to upload it.
Create the pfcUploadOptions object using the method pfcUploadOptions.Create().
The methods available for setting the upload options are described in the following section.
CheckIn
After you have finished working on objects in your workspace, you can share the design changes with other users. The checkin
operation copies the information and files associated with all changed objects from the workspace to the Windchill database.
Methods and Properties Introduced:
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The method pfcServer.CheckinObjects() checks in an object into the database. The object to be checked in must be present in the current Creo Parametric session. Changes made to the object are not included unless you save the object to the workspace using the method pfcModel.Save() before you check it in.
If you pass NULL as the value of the options parameter, the checkin operation is similar to the Auto Check-In option in Creo Parametric. For more details on Auto Check-In, refer to the online help for Creo Parametric.
Use the method pfcCheckinOptions.Create() to create a new pfcCheckinOptions object.
By using an appropriately constructed options argument, you can control the checkin operation. Use the APIs listed above to access and modify the checkin options. The
checkin options are as follows:
| • | DefaultFolder—Specifies the default folder location on the server for the automatic checkin operation. |
| • | NonDefaultFolderAssignment—Specifies the folder location on the server to which the objects will be checked in. |
| • | AutoresolveOption—Specifies the option used for auto-resolving missing references. These options are defined in the pfcServerAutoresolveOption enumerated type , and are as follows:
|
| • | Baseline—Specifies the baseline information for the objects upon checkin. The baseline information for a checkin operation is as follows:
The default format for the baseline name and baseline number is Username + time (GMT) in milliseconds.
|
| • | KeepCheckedout—If the value specified is true, then the contents of the selected object are checked into the Windchill server and automatically checked out again for further modification. |
Retrieval
Standard Web.Link provides several methods that are capable of retrieving models. When using these methods with Windchill servers, remember that these methods do not check out the object to allow modifications.
Methods Introduced:
The methods pfcBaseSession.RetrieveModel(), pfcBaseSession.RetrieveModelWithOpts(), and pfcBaseSession.OpenFile() load an object into a session given its name and type. The methods search for the object in the active workspace, the local
directory, and any other paths specified by the search_path configuration option.
Checkout and Download
To modify an object from the commonspace, you must check out the object. The process of checking out communicates your intention
to modify a design to the Windchill server. The object in the database is locked, so that other users can obtain read-only copies of the object, and are prevented
from modifying the object while you have checked it out.
Checkout is often accompanied by a download action, where the objects are brought from the server-side workspace to the local
workspace cache. In Web.Link, both operations are covered by the same set of methods.
Methods and Properties Introduced:
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The method pfcServer.CheckoutObjects() checks out and optionally downloads the object to the workspace based on the configuration specifications of the workspace.
The input arguments of this method are as follows:
| • | Mdl—Specifies the object to be checked out. This is applicable if the model has already been retrieved without checking it out. |
| • | File—Specifies the top-level object to be checked out. |
| • | Checkout—The checkout flag. If you specify the value of this argument as true, the selected object is checked out. Otherwise, the object is downloaded without being checked out. The download action enables you to bring read-only copies of objects into your workspace. This allows you to examine the object without locking it. |
| • | Options—Specifies the checkout options object. If you pass NULL as the value of this argument,, then the default Creo Parametric checkout rules apply. Use the method pfcCheckoutOptions.Create() to create a new pfcCheckoutOptions object. |
Use the method pfcServer.CheckoutMultipleObjects() to check out and download multiple objects to the workspace based on the configuration specifications of the workspace. This
method takes the same input arguments as listed above, except for Mdl and File. Instead it takes the argument Files that specifies the sequence of the objects to check out or download.
Note
Web.Link methods do not support AS_STORED configuration.
By using an appropriately constructed options argument in the above functions, you can control the checkout operation. Use the APIs listed above to modify the checkout
options. The checkout options are as follows:
| • | Dependency—Specifies the dependency rule used while checking out dependents of the object selected for checkout. The types of dependencies
given by the pfcServerDependency enumerated type are as follows:
|
| • | IncludeInstances—Specifies the rule for including instances from the family table during checkout. The type of instances given by the pfcServerIncludeInstances enumerated type are as follows:
|
| • | SelectedIncludes—Specifies the sequence of URLs to the selected instances, if IncludeInstances is of type SERVER_INCLUDE_SELECTED. |
| • | Version—Specifies the version of the checked out object. If this value is set to NULL, the object is checked out according to the current workspace configuration. |
| • | Download—Specifies the checkout type as download or link. The value download specifies that the object content is downloaded and checked out, while link specifies that only the metadata is downloaded and checked out. |
| • | Readonly—Specifies the checkout type as a read-only checkout. This option is applicable only if the checkout type is link. |
The following truth table explains the dependencies of the different control factors in the method pfcServer.CheckoutObjects() and the effect of different combinations on the end result.
|
Argument checkout in pfc
Server.Checkout Objects |
pfcCheckoutOptions.SetDownload
|
pfcCheckoutOptions.SetReadonly
|
Result
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
true
|
true
|
NA
|
Object is checked out and its content is downloaded.
|
|
true
|
false
|
NA
|
Object is checked out but content is not downloaded.
|
|
false
|
NA
|
true
|
Object is downloaded without checkout and as read-only.
|
|
false
|
NA
|
false
|
Not supported
|
Undo Checkout
Method Introduced:
Use the method pfcServer.UndoCheckout() to undo a checkout of the specified object. When you undo a checkout, the changes that you have made to the content and metadata
of the object are discarded and the content, as stored in the server, is downloaded to the workspace. This method is applicable
only for the model in the active Creo Parametric session.
Import and Export
Web.Link provides you with the capability of transferring specified objects to and from a workspace. Import and export operations
must take place in a session with no models. An import operation transfers a file from the local disk to the workspace.
Methods and Properties Introduced:
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
The methodpfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS() exports the specified objects from the current workspace to a disk in a linked session of Creo Parametric.
The method pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() imports the specified objects from a disk to the current workspace in a linked session of Creo Parametric.
Both pfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS() and pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() allow you to specify a dependency criterion to process the following items:
| • | All external dependencies |
| • | Only required dependencies |
| • | No external dependencies |
Both pfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS() and pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() return the messages generated during the export or import operation in the form of the pfcWSImportExportMessages object. Use the APIs listed above to access the contents of a message. The message specified by the pfcWSImportExportMessage object contains the following items:
| • | Description—Specifies the description of the problem or the message information. |
| • | FileName—Specifies the object name or the name of the object path. |
| • | MessageType—Specifies the severity of the message in the form of the pfcWSImportExportMessageType enumerated type. The severity is one of the following types:
|
| • | Resolution—Specifies the resolution applied to resolve a conflict that can be overridden. This is applicable when the message is of the type WSIMPEX_MSG_CONFLICT. |
| • | Succeeded—Determines whether the resolution succeeded or not. This is applicable when the message is of the type WSIMPEX_MSG_CONFLICT. |
The method pfcBaseSession.SetWSExportOptions() sets the export options used while exporting the objects from a workspace in the form of the pfcWSExportOptions object. Create this object using the method pfcWSExportOptions.Create(). The export options are as follows:
| • | Include Secondary Content—Indicates whether or not to include secondary content while exporting the primary Creo Parametric model files. Use the property pfcWSExportOptions.IncludeSecondaryContent to set this option. |
File Copy
Web.Link provides you with the capability of copying a file from the workspace or target folder to a location on the disk and vice-versa.
Methods Introduced:
Use the method pfcBaseSession.CopyFileToWS() to copy a file from the disk to the workspace. The file can optionally be added as secondary content to a given workspace
file. If the viewable file is added as secondary content, a dependency is created between the Creo Parametric model and the viewable file.
Use the method pfcBaseSession.CopyFileFromWS() to copy a file from the workspace to a location on disk.
When importing or exporting Creo Parametric models, PTC recommends that you use methods pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() and pfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS(), respectively, to perform the import or export operation. Methods that copy individual files do not traverse Creo Parametric model dependencies, and therefore do not copy a fully retrievable set of models at the same time.
Additionally, only the methods pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() and pfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS() provide full metadata exchange and support. That means pfcBaseSession.ImportToCurrentWS() can communicate all the Creo Parametric designated parameters, dependencies, and family table information to a PDM system while pfcBaseSession.ExportFromCurrentWS() can update exported Creo Parametric data with PDM system changes to designated and system parameters, dependencies, and family table information. Hence PTC recommends
the use of pfcBaseSession.CopyFileToWS() and pfcBaseSession.CopyFileFromWS() to process only non-Creo Parametric files.
Server Object Status
Methods Introduced:
The methods described in this section verify the current status of the object in the workspace. The method pfcServer.IsObjectCheckedOut() specifies whether the object is checked out for modification. The value true indicates that the specified object is checked out to the active workspace.
The value false indicates one of the following statuses:
| • | The specified object is not checked out |
| • | The specified object is only uploaded to the workspace, but was never checked in |
| • | The specified object is only saved to the local workspace cache, but was never uploaded |
The method pfcServer.IsObjectModified() specifies whether the object has been modified in the workspace. This method returns true if the object was modified locally.
Conflicts During Server Operations
An exception is provided to capture the error condition while performing the following server operations using the specified
APIs:
|
Operation
|
API
|
|---|---|
|
Checkin an object or workspace
|
pfcServer.CheckinObjects()
|
|
Checkout an object
|
pfcServer.CheckoutObjects()
|
|
Undo checkout of an object
|
pfcServer.UndoCheckout()
|
|
Upload object
|
pfcServer.UploadObjects()
|
|
Download object
|
pfcServer.CheckoutObjects (with download as true)
|
|
Delete workspace
|
pfcServerLocation.DeleteWorkspace
|
|
Remove object
|
pfcServer.RemoveObjects()
|
These APIs throw a common exception pfcXToolkitCheckoutConflict if an error is encountered during server operations. The exception description will include the details of the error condition.
This description is similar to the description displayed by the Creo Parametric HTML user interface in the conflict report.